Setting the Blending Mode
This menu allows you to specify the blending mode of layers.

Blending Modes on the Layer Palette
The following blending modes can be set on the [Layer] palette.
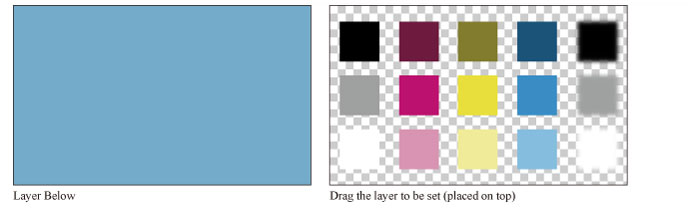
In this section, the upper layer on which the blending mode is set is called the "set layer" and the layer below it is called the "layer below". The figure for each item shows the effect of the set blending mode when the following layer configuration is used.
|
|
[Darker color], [Lighter color], [Vivid light], [Linear light], [Pin light], [Hard mix], [Exclusion], [Divide], [Hue], [Saturation], [Color] and [Brightness] blending modes have been added to Ver. 1.6.2. Layers with these new blending modes will not be shown correctly in Clip Studio Paint Ver 1.5.4 and earlier. |
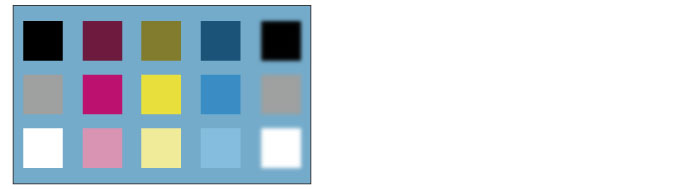
Normal
The set layer is simply placed over the layer below.
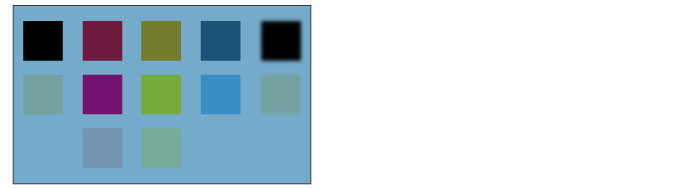
Darken
The RGB values of the set layer and the layer below are compared and the color with the lower value is displayed.
For example, if a color where R = 100, G = 200 and B = 25 is blended with one where R = 10, G = 255 and B = 90, the blended color uses the lowest of each RGB value: R = 10, G = 200 and B = 25.
Multiply
The RGB values of the set layer are multiplied by those on the layer below. After blending, the colors are darker than the originals.
For example, if a color where R = 100, G = 200 and B = 25 is blended with one where R = 10, G = 255 and B = 90, the R values of 100 and 10 from the two layers are multiplied together and then divided by 255 to obtain the blended color value. The G and B values are calculated in the same way to obtain the blended values.
If the set layer is white (R = 255, G = 255, B = 255), the color of the layer below is used as it is.

Color burn
Produces an effect similar to the "burn" in silver halide photography. The colors used in images on the layer below are first darkened to increase contrast, and then combined with the colors used on the layer being configured.
If the set layer is white (R = 255, G = 255, B = 255), the color of the layer below is used as it is.
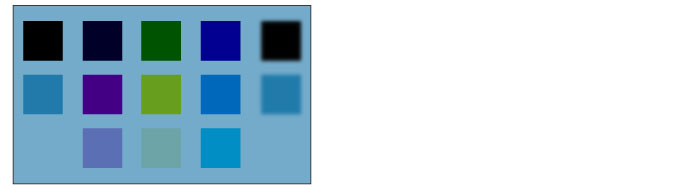
Linear burn
The colors in the layer below are first darken, and then combined with the colors in the layer being configured.
If the set layer is white (R = 255, G = 255, B = 255), the color of the layer below is used as it is.
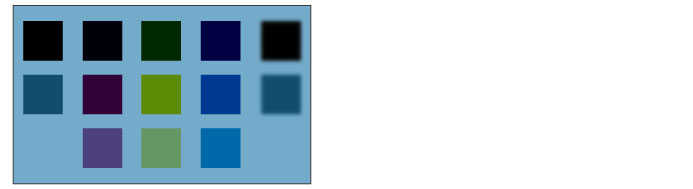
Subtract
The RGB values of the set layer are subtracted from those of the layer below. After blending, the colors are darker than the originals.
For example, if R = 10, G = 255 and B = 90 on the layer below and R = 100, G = 200 and B = 25 on the set layer, the R value of the set layer (100) is subtracted from that of the layer below (10). Because the result is a negative value, 0 is set as the blended R value. The G and B values are calculated in the same way to obtain the blended values.
If the set layer is black (R = 0, G = 0, B = 0), the color of the layer below is used as it is.

Lighten
The RGB values of the set layer and the layer below are compared and the color with the higher value is displayed. For example, if a color where R = 100, G = 200 and B = 25 is blended with one where R = 10, G = 255 and B = 90, the blended color uses the highest of each RGB value: R = 100, G = 255 and B = 90.

Screen
The colors used in the layer below are inverted and then multiplied with those on the set layer. After blending , the colors are brighter than the originals.
If the set layer is black (R = 0, G = 0, B = 0), the color of the layer below is used as it is. If the set layer is white (R = 255, G = 255, B = 255), it remains white.

Color dodge
As with "dodge" in silver halide photography, the colors used in the lower layer becomes brighter and the contrast, lower.
If the set layer is black (R = 0, G = 0, B = 0), the color of the layer below is used as it is.

Dodge (Glow)
Produces stronger effect on semi-transparent areas than [Color dodge].
If the set layer is black (R = 0, G = 0, B = 0), the color of the layer below is used as it is.

Add
The RGB values of the set layer are added to those of the layer below. After blending , the colors are brighter than the originals.
For example, if R = 10, G = 255 and B = 90 on the layer below and R = 100, G = 200 and B = 25 on the set layer, the R value of the set layer (100) is added to that of the layer below (10). The blended value is 110. The G and B values are calculated in the same way to obtain the blended values. If the result is over 255, 255 is set as the blended value.
If the set layer is black (R = 0, G = 0, B = 0), the color of the layer below is used as it is.

Add (Glow)
Produces stronger effect on semi-transparent areas than [Add].
If the set layer is black (R = 0, G = 0, B = 0), the color of the layer below is used as it is.

Overlay
[Multiply] or [Screen] is applied depending on the color of the layer below. After combine, bright areas are brighter and dark areas, darker.

Soft light
The results differ depending on the brightness of the set layer. When the overlapping color is brighter than 50% gray, the result is brighter than the original color, as in the dodge effect.
When the overlapping color is darker than 50% gray, the result is darker than the original color, as in the burn effect. When the overlapping color is 50% gray, the color of the layer below is used as it is.

Hard light
The results differ depending on the brightness of the set layer. When the overlapping color is brighter than 50% gray, the result is a brighter color resembling the effect of [Screen].
When the overlapping color is darker than 50% gray, the result is a darker color resembling the effect of [Multiply]. When the overlapping color is 50% gray, the color of the layer below is used as it is.

Difference
The color of the set layer is subtracted from the layer below and the absolute value of the difference is blended with the color of the layer below.

Vivid light
The contrast is strengthened or weakened depending on the color of the set layer. If the set layer is brighter than 50% gray, burn is applied and the image is brightened. If it is darker than 50% gray, dodge is applied and the contrast of the image is strengthened.
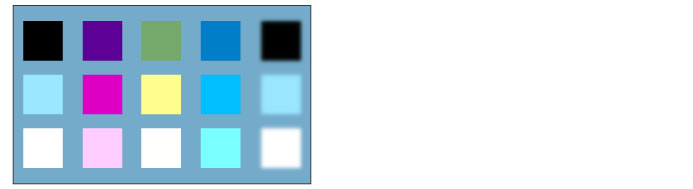
Linear light
The brightness is increased or decreased depending on the color of the set layer. If the set layer is brighter than 50% gray, the image is brightened. If it is darker than 50% gray, the image is darkened.

Pin light
The colors of the image are replaced depending on the color of the set layer. If the set layer is brighter than 50% gray, the color of the layer below is only replaced with that of the set layer in the areas where the color of the layer below is darker. If the set layer is darker than 50% gray, the color of the layer below is only replaced with that of the set layer in the areas where the color of the layer below is brighter.
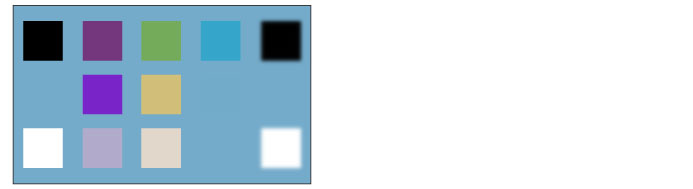
Hard mix
The RGB values of the set layer are added to those of the layer below. If the total of an RGB value is higher than 255, it is converted to 255. If the total of an RGB value is lower than 255, it is converted to 0.
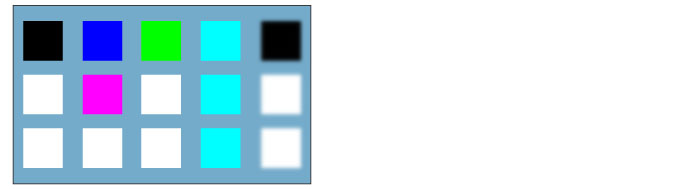
Exclusion
An effect similar to [Difference], except with a lower contrast.
If the set layer is white, the colors of the layer below are inverted when blending. If the set layer is black, the color of the layer below is used as it is.
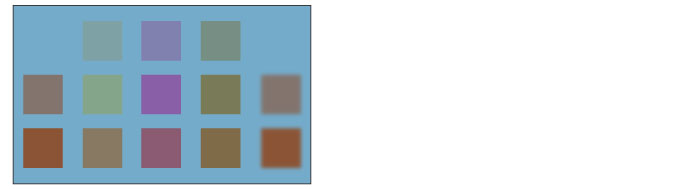
Darker color
The brightness of the set layer and the layer below are compared, and the color with the lower value is displayed.
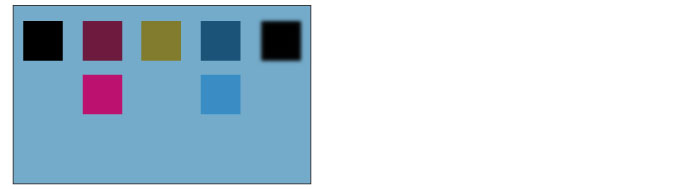
Lighter color
The brightness of the set layer and the layer below are compared, and the color with the lower value is displayed.

Divide
The RGB values of the layer below are multiplied by 255 and then divided by the RGB values of the set layer.
For example, if R = 10, G = 255 and B = 90 on the layer below and R = 100, G = 200 and B = 25 on the set layer, the R value of the layer below (10) is multiplied by 255 (=2550) and then divided by the R value of the set layer (100). The blended value is 13. The G and B values are calculated in the same way to obtain the blended values. If the result is over 255, 255 is set.
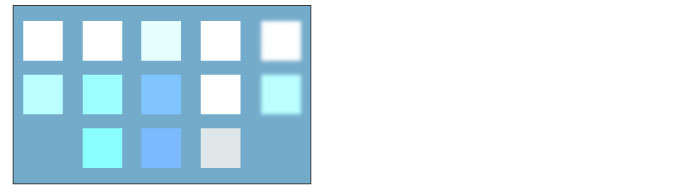
Hue
The hue of the set layer is applied while maintaining the brightness and saturation of the layer below.
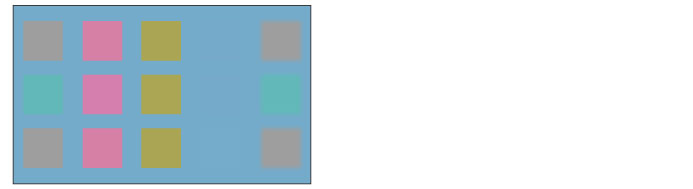
Saturation
The saturation of the set layer is applied while maintaining the brightness and hue of the layer below.
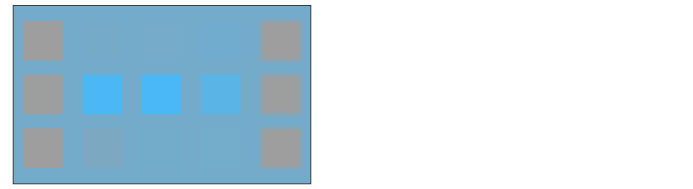
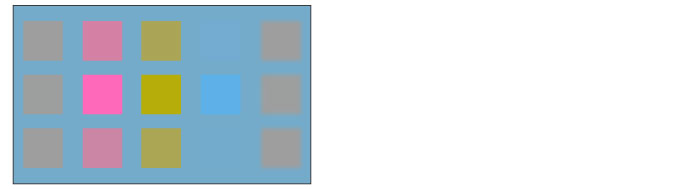
Color
The hue and saturation of the set layer are applied while maintaining the brightness of the layer below.
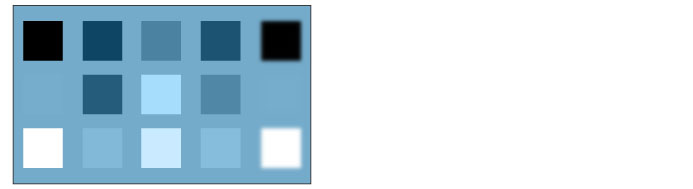
Brightness
The brightness of the set layer is applied while maintaining the hue and saturation of the layer below.
Through
Applies the effects and layer blending modes of the tonal correction layers stored in the layer folder also to layers outside the layer folder. [Through] is available only when a layer folder is selected.